Running head: DREAM COMPANY FIT
Topic: DREAM COMPANY FIT
Name:
Course:
Instructor’s Name:
Date:
Part I: Organizational Structure and Culture
Organizational structures are typical activities directed towards the achievement of a company’s objective. Organization structures should be designed to show how companies design their structure to match the dynamism and uncertainty of their environment. They can be structured in many different ways to achieve various objectives. This paper deals with a description of the different organizational structures and their application in the company.
A mechanistic structure suits companies that operate in stable environments while companies facing a dynamic environment- an environment that changes regularly- may have to use an organic structure. This is because companies use the organic structure process and distribute information faster within the organization resulting in an increased ability to respond to changes in the environment. Mechanistic structures on the other hand may serve their effectiveness for companies operating in a more certain environment. The reason for this is, they may not need to make decisions quickly since many operating procedures may be centralized or formalized as there is no constant change.
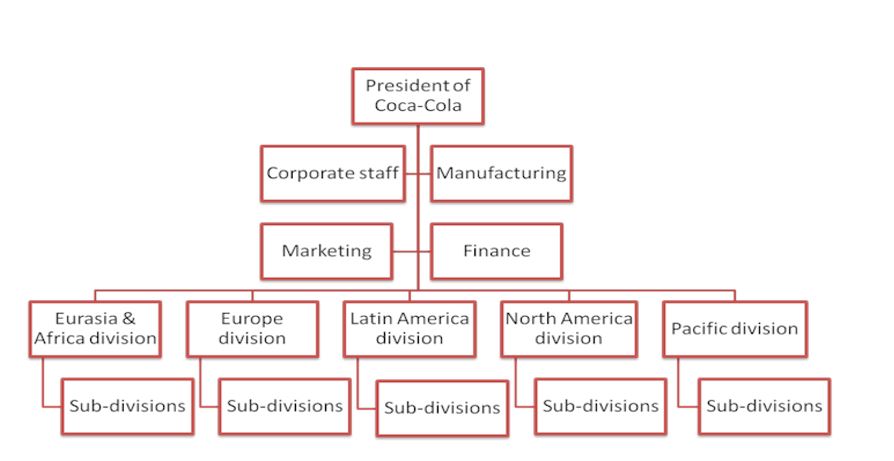
Different elements of the organization structure have been utilized in the Coca-Cola Company as has been utilized below in the chart. Different tasks are divided to separate divisions in each continent with direct reports to the overall chief executive officer (CEO). Formalization is strongly used as all products and services have to be standardized around the continent to reflect the company’s uniformity and drive in conformity.
A simple organizational structure is one in which the owner or manager makes all major decisions and directly monitors all activities. This structure is most used for medium-scale or small companies with less than 100 employees. A bureaucratic organization is one where there are clear commands and defined roles and responsibilities. They are better suited for large-scale organizations.
In this case, the Coca-Cola Company utilizes the bureaucratic organization structure since each region has different needs and wants for the company’s products. The company also uses the organic organizational structure as the product they produce faces uncertainties such as high competition and changing consumer preferences.
Coca-Cola is an ethnocentric company as all operations are similar locally and internationally. They operate and sell the same brand regardless of country and region with tight control over operations from the head office. Every organization has not only a structure but also a culture which represents the way in which an organization does things including patterns of behavior and relationships between their partners and employees.
The most important aspect of the Coca-Cola Company is the emphasis on teamwork and empowerment. The company sees the employees as the most important asset. Motivated employees provide the engine that drives the company’s growth. It helps to make the people make valued and in turn contribute ideas and are innovative. They are encouraged to voice opinions for the growth and betterment of the company worldwide.
By maintaining this innovative culture, the Coca-Cola Company is able to depend on a high-quality workforce that helps maintain strong brand recognition in the world market. The open communication models provide the means to support culture-based relationships which are enhanced by frequent communication channels throughout the year.
Coca-Cola expresses value in leadership, passion, collaboration, diversity, quality, accountability and integrity. The company possesses a worldwide team that is rich in talent ideas and diversity in people. They have workplace strategies to retain and develop diverse talents.
-
Wolcott and Lippitz Taxonomy of Corporate Entrepreneurship
Introduction: Understanding Corporate Entrepreneurship In today’s dynamic business landscape, the concept of corporate entrepreneurship has gained significant traction. But what exactly does it entail? Let’s delve into the essence of Wolcott and Lippitz Taxonomy of Corporate Entrepreneurship before exploring its various models and implications in the current business environment. Defining Corporate Entrepreneurship Corporate entrepreneurship embodies…
-
Schumpeter’s Equilibrium Destruction Theory: Unraveling the Dynamics of Strategic Entrepreneurship
Delving into the intersection of strategic management and entrepreneurship, the theories of Joseph Schumpeter illuminate the process of economic growth through innovation. This article explores Schumpeter’s equilibrium destruction theory, analyzing how entrepreneurs catalyze economic dynamism by identifying and seizing opportunities amidst competition. Navigating the Dynamics of Modern Business Within the realm of strategic management, Joseph…
-
Understanding Ansoff’s Growth Vector Matrix
In the ever-evolving landscape of modern business, staying stagnant is not an option. As the Red Queen famously said, “It takes all the running you can do to keep in the same place.” In today’s global economy, this sentiment rings truer than ever. To merely maintain relevance, businesses must continuously adapt, innovate, and grow. H.…
Part II: Person-Organization Fit
According to Kristof 2009 a Person-organization fit perspective has been utilized in analyzing how a person would function well in an organization. It assumes that this would depend on the nature of the task or the organization. There are two distinct ways of defining fit; Person job fit and person-organization fit. This chapter discusses the person-organization fit. Fit is measured in different major dimensions. They are, Innovation, Stability, Orientation towards people (fair and supportive), Orientation towards outcomes (results-oriented, achievement-oriented), Easygoing vs. aggressive, Attention to detail and Team orientation.
In relation to the Coca-Cola Company, all the mentioned traits are needed to make a good fit for the company. The diverse nature of the company and the products it produces has a bearing on the kind of employees they interest themselves with and the culture of the company as well. The traits that make me a good fit for the company are the orientation towards outcome and the team orientation which are the key ingredients that the Coca-Cola Company looks for.
.The combination of these two traits with the openness to experience (i.e. imaginative, creative, sophisticated, refined, curious and complex) and the extraversion abilities (talkative, sociable, assertive, dominant, and passionate) are the ingredients that I possess and can be effective in the company. Personality is the combination of attitudinal, emotional and behavioural response patterns of an individual which can be measured with different varieties of tests.
To be an extravert means to be concerned with more practical realities than with inner thoughts. A person who finds social situations more rewarding than introverts because they are more sensitive to the rewards associated with being extraverted. Their thought is directed outwards and is marked by interests for others and general external reality. These traits help them adapt to different situations in the business and social worlds.
To have an open-to-experience attitude means being creative enough in an ever-changing and dynamic environment. Thus openness can be as a personality trait which consists of certain habits and tendencies that are grouped together. The Coca-Cola group needs a person who can be open to new ideas that may impact business growth as opposed to traditional thinkers.
References
Cheri, L., O. (2009) Perspectives on organizational fit. New York: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
